Fossilised cat-sized reptile found in Scotland was ‘early relative of pterosaurs’
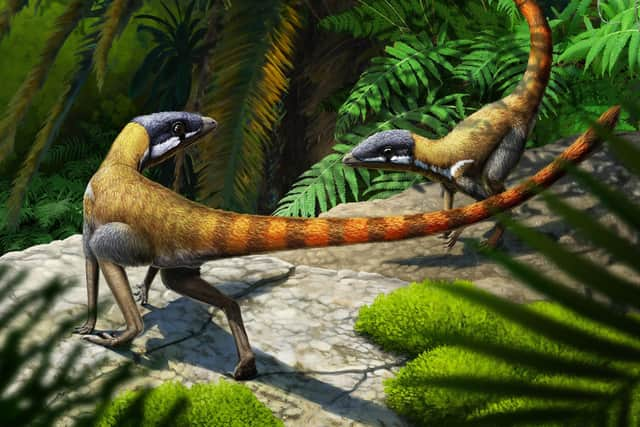
The small cat-sized creature, named Scleromochlus taylori, is thought to have roamed the planet somewhere between 240 to 210 million years ago.
Pterosaurs were one of the first animals to evolve powered flight and the researchers believe that Scleromochlus may hold a key place in its evolutionary tree.
Advertisement
Hide AdAdvertisement
Hide AdThe palaeontologists said their findings, published in the journal Nature, could help shed more light on the origins of pterosaurs.


Sterling Nesbitt, an associate professor at Virgina Tech in the US and one of the authors on the study, said: “Pterosaurs were the first vertebrates to evolve powered flight and for nearly two centuries, we did not know their closest relatives.
“Now we can start filling in their evolutionary history with the discovery of tiny close relatives that enhance our knowledge about how they lived and where they came from.”
Pterosaurs were close cousins of dinosaurs who evolved on a separate branch of the reptile family tree.
Some species were as large as fighter jets while others were as small as paper planes.
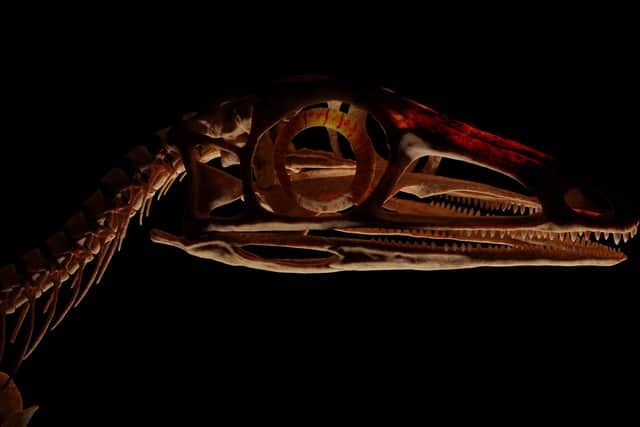

Scleromochlus, meanwhile, was no more than 20cm long.
It had a large head, a long tail, a short neck, a slender body, and stood on spindly legs.
Fossilised remains of the creature were first discovered more than 100 years ago near Elgin in Morayshire.
However, the fossil was poorly preserved in sandstone so scientists were unable to study its anatomical features in detail.


Advertisement
Hide AdAdvertisement
Hide AdThis led to debates amongst experts as to whether Scleromochlus was closer to pterosaurs or did it have more in common with dinosaurs in the evolutionary tree.
First author Dr Davide Foffa, research associate at National Museums Scotland – and now a research fellow at the University of Birmingham, said: “It’s exciting to be able to resolve a debate that’s been going on for over a century, but it is far more amazing to be able to see and understand an animal which lived 230 million years ago and its relationship with the first animals ever to have flown.
“This is another discovery which highlights Scotland’s important place in the global fossil record, and also the importance of museum collections that preserve such specimens, allowing us to use new techniques and technologies to continue to learn from them long after their discovery.”
The researchers used a CT scan – an imaging technique usually used by medical professionals to obtain internal images of the body – to reconstruct the skeleton of Scleromochlus.
The findings suggest the reptile may have belonged to Pterosauromorpha – the clade that includes pterosaurs and a group of small reptiles called lagerpetids.
The experts believe their work supports the hypothesis that pterosaurs evolved from small, likely two-legged ancestors.
Comments
Want to join the conversation? Please or to comment on this article.